Thermal drones are revolutionizing industries, combining cutting-edge thermal imaging technology with the versatility of aerial systems. These drones are equipped with thermal cameras that detect heat signatures, enabling users to perform tasks like inspections, surveillance, and search-and-rescue operations with unparalleled accuracy. Get Here More Free Shipping Products
What Is a Thermal Drone?
A thermal drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) fitted with a thermal imaging camera. These cameras capture infrared radiation, making it possible to “see” heat, even in complete darkness or through obstacles like smoke and fog. This unique capability makes thermal drones indispensable in various fields, including construction, agriculture, security, and emergency services.

Why Choose a Thermal Drone?
Thermal drones are a game-changer for professionals and hobbyists alike. Here’s why:
- Enhanced Inspections
Whether you’re inspecting power lines, solar panels, or roofs, thermal drones provide detailed heat maps to identify issues like leaks, overheating components, or structural weaknesses. - Improved Safety
By allowing inspections from a distance, thermal drones reduce the need for risky manual checks in hazardous environments like high altitudes or active fire zones. - Search-and-Rescue Operations
Thermal imaging can locate missing persons or animals by detecting body heat, even in dense forests or after natural disasters. - Wildlife Monitoring and Conservation
Track animal movements, study habitats, and identify poachers—all without disturbing the environment. - Agricultural Benefits
Monitor crop health by identifying heat stress or irrigation issues, leading to optimized yields and resource management.

Key Features of Thermal Drones
- High-Resolution Thermal Cameras
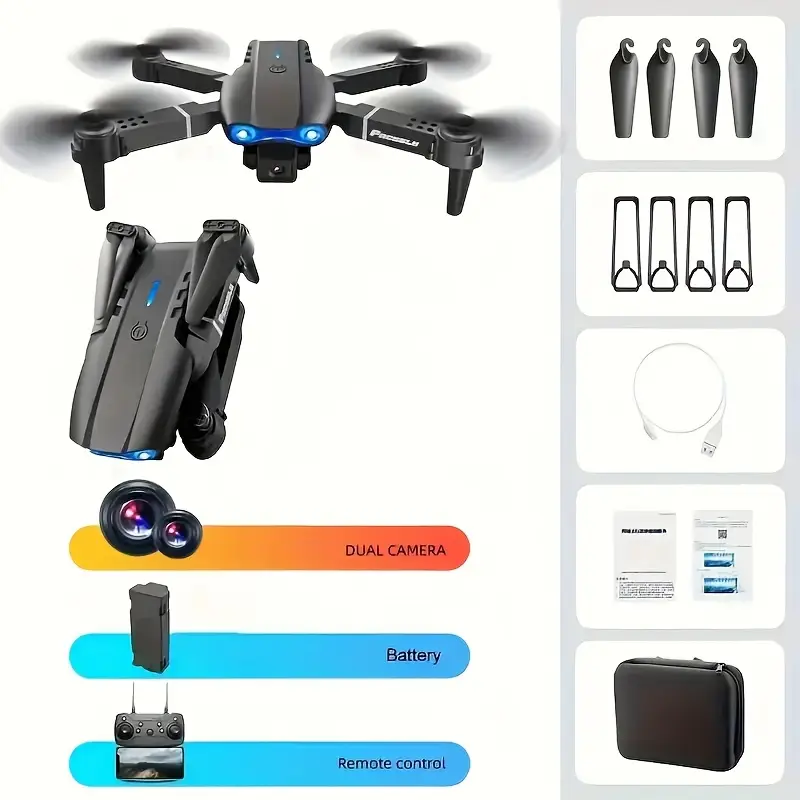
Advanced sensors offer crisp, clear heat maps for detailed analysis. - Dual Camera Systems
Many thermal drones include both thermal and visual cameras, providing users with both heat maps and standard imagery. - Long Flight Times
Modern thermal drones boast extended battery life, allowing for thorough inspections or patrols. - GPS and Autonomous Capabilities
Features like GPS mapping and automated flight paths simplify complex operations, saving time and effort. - Real-Time Data Transmission
View and analyze thermal data instantly on connected devices, ensuring quick decision-making.

Ready to harness the power of thermal imaging? Shop NOW for high-quality thermal drones and to elevate your workflow with the latest technology.
Thermal drones are no longer a luxury—they’re an essential tool for precision, safety, and efficiency. Don’t miss out on this transformative technology!
Let me provide a comprehensive FAQ about thermal drones that covers both basic concepts and advanced applications. I’ll write this in a clear, detailed format that builds understanding progressively.

Frequently Asked Questions: Thermal Drones
1. What exactly is a thermal drone and how does it work?
A thermal drone combines an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) with a thermal imaging camera that detects infrared radiation emitted by objects and surfaces. The camera sensor measures temperature variations and creates a visual heat map, where different colors represent different temperature levels. The thermal imaging system typically operates independently of visible light, making these drones effective both day and night. The captured thermal data is processed in real-time and can be viewed live or recorded for later analysis.
2. What are the primary applications of thermal drones?
Thermal drones serve numerous industries with their unique capabilities. In search and rescue operations, they can locate missing persons by detecting body heat signatures, even in darkness or through foliage. Building inspectors use them to identify heat leaks, moisture intrusion, and electrical issues in structures. Agricultural professionals employ thermal drones to monitor crop health by detecting temperature variations that might indicate stress or disease. They’re also valuable in wildlife conservation, firefighting, and industrial inspection of equipment and infrastructure.
3. How accurate are thermal drone temperature measurements?
Modern thermal drones can achieve remarkable accuracy, typically within 1-2 degrees Celsius when properly calibrated. However, this accuracy depends on several factors: the quality of the thermal sensor, the drone’s distance from the target, atmospheric conditions, and proper calibration. Professional-grade thermal drones often include radiometric capabilities, meaning they can provide actual temperature measurements for each pixel in the image, rather than just relative temperature differences.
4. What environmental factors affect thermal drone performance?
Thermal drone effectiveness can be impacted by various environmental conditions. Heavy rain or snow can interfere with readings by creating thermal barriers between the sensor and the target. Extreme ambient temperatures can affect the contrast in thermal images. Solar loading (heat absorbed from direct sunlight) can create false readings, which is why many thermal inspections are conducted early morning or late evening. Wind can affect both drone stability and thermal readings, while humidity levels can influence infrared transmission through the air.
5. What kind of training is required to operate a thermal drone professionally?
Professional thermal drone operation requires multiple skill sets. Operators need standard drone pilot certification (like the FAA Part 107 in the United States) plus specialized training in thermal imaging interpretation. This includes understanding thermal physics, camera operation, environmental factors affecting readings, and industry-specific applications. Many operators also pursue additional certifications in thermography and specific software platforms used for data analysis.

6. How do thermal drones compare to traditional inspection methods?
Thermal drones offer several advantages over traditional inspection methods. They can quickly survey large areas that would take hours or days to inspect manually. They can safely access dangerous or hard-to-reach locations without putting personnel at risk. The ability to capture comprehensive thermal data from multiple angles provides more thorough documentation than ground-based thermal cameras. However, they may have limitations in terms of close-up detail compared to hands-on inspection methods.
7. What are the latest technological advances in thermal drone systems?
Recent advances include higher-resolution thermal sensors, improved image processing algorithms, and artificial intelligence integration for automatic anomaly detection. Dual sensor systems combining thermal and visible light cameras enable better context and analysis. Advanced radiometric capabilities now allow for more precise temperature measurements and better data integration with other inspection tools. Some systems also feature real-time 3D mapping capabilities, combining thermal data with spatial information.
8. What considerations should be made when choosing a thermal drone system?
Selection criteria should include the specific application requirements, sensor resolution and sensitivity, flight time capabilities, and environmental operating conditions. The drone’s payload capacity must accommodate the thermal camera system while maintaining adequate flight time. Software compatibility for data processing and analysis is crucial. Consider also the level of training and support provided by the manufacturer, as well as the system’s upgradeability to accommodate future technological advances.
9. How is the data from thermal drones processed and analyzed?
Thermal drone data analysis typically involves specialized software that can process both thermal and visual imagery. These programs can create detailed reports, perform quantitative analysis, and generate 3D thermal models. Many systems now incorporate machine learning algorithms to automatically identify anomalies or patterns in the thermal data. The software often allows for data export in various formats for integration with other analysis tools or client reporting systems.
10. What are the regulatory considerations for thermal drone operations?
Regulatory compliance involves multiple aspects. Beyond standard drone operation regulations (altitude restrictions, flight zones, certification requirements), thermal drone operators must consider privacy laws when capturing thermal data of private property. Some industries have specific requirements for thermal inspection documentation and reporting. Additionally, export controls may apply to certain high-end thermal imaging systems, requiring special permits for international operations or sales.





Your enthusiasm is contagious. It is difficult not to become enthused about the topics you debate.
I appreciate the distinctive perspective you present in your writing.